Introduction
As environmental concerns rise and water scarcity becomes a global issue, STP Plants (Sewage Treatment Plants) play a critical role in sustainable development. These systems are designed to treat wastewater from homes, commercial buildings, and industries, making the water reusable and safe for the environment.
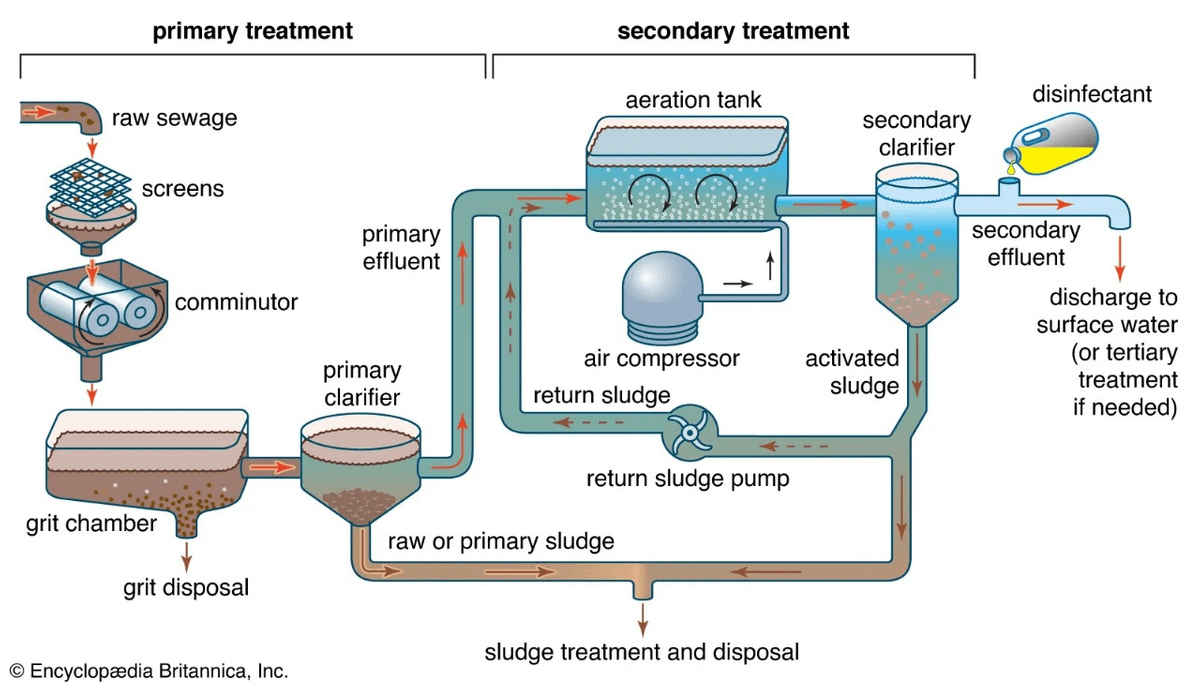
What is an STP Plant?
An STP Plant is a facility that treats domestic sewage and wastewater, removing contaminants and converting it into clean, reusable water. It helps reduce pollution, conserves water, and ensures compliance with environmental regulations.

How Does an STP Plant Work?
Sewage treatment typically follows three key stages:
-
Primary Treatment
Large solids and floating materials are separated, and oil or grease is removed. -
Secondary Treatment
Biological processes are used to break down organic matter using aerobic bacteria. -
Tertiary Treatment
Advanced filtration and disinfection remove remaining impurities, making the water suitable for reuse (e.g., gardening, flushing, cooling).
Where Are STP Plants Used?
- Residential Societies
- Hospitals & Hotels
- Commercial Complexes
- Factories & Industries
- Educational Institutions
In many countries, including India, STP plants are mandatory for establishments generating more than 20 KLD (kiloliters per day) of wastewater.
Benefits of STP Plants
- 🌱 Water Reuse: Treated water can be reused for non-potable applications.
- 🌍 Eco-Friendly: Reduces water pollution and conserves natural water bodies.
- ✅ Legal Compliance: Fulfills pollution control board norms.
- 💰 Cost-Effective: Long-term savings on water bills.
- 🏢 Green Certification: Adds value to eco-friendly infrastructure.
Conclusion
Installing an STP Plant is not just a legal necessity but an environmental responsibility. Whether you're a builder, business owner, or part of a housing society, investing in sewage treatment is a step towards a cleaner and greener future.